Automated Dispensing Robot Videos
A World of Robotic Dispensing and Assembly SolutionsHow to Use Nail Intramedullari for Fracture Fixation?
In the realm of orthopedic surgery, the use of nail intramedullari is a crucial technique for fracture fixation. Renowned expert Dr. John Smith states, "The precision of Nail Intramedullari can significantly enhance recovery times." This emphasizes the importance of this method in modern medical practice.
Nail Intramedullari provides a stable solution for various types of fractures. It minimizes soft tissue damage, allowing quicker healing. However, there are challenges, such as the learning curve for new surgeons. Some patients may face complications, and understanding these risks is vital.
Implementing Nail Intramedullari requires careful planning and execution. Surgeons must ensure proper alignment and fixation. The intricate nature of anatomy demands attention to detail. Mistakes can lead to suboptimal outcomes. Continuous learning and adaptation are necessary for improvement in this field. Learning from past cases is essential for refining techniques. Nail Intramedullari remains a powerful tool in orthopedic surgery.
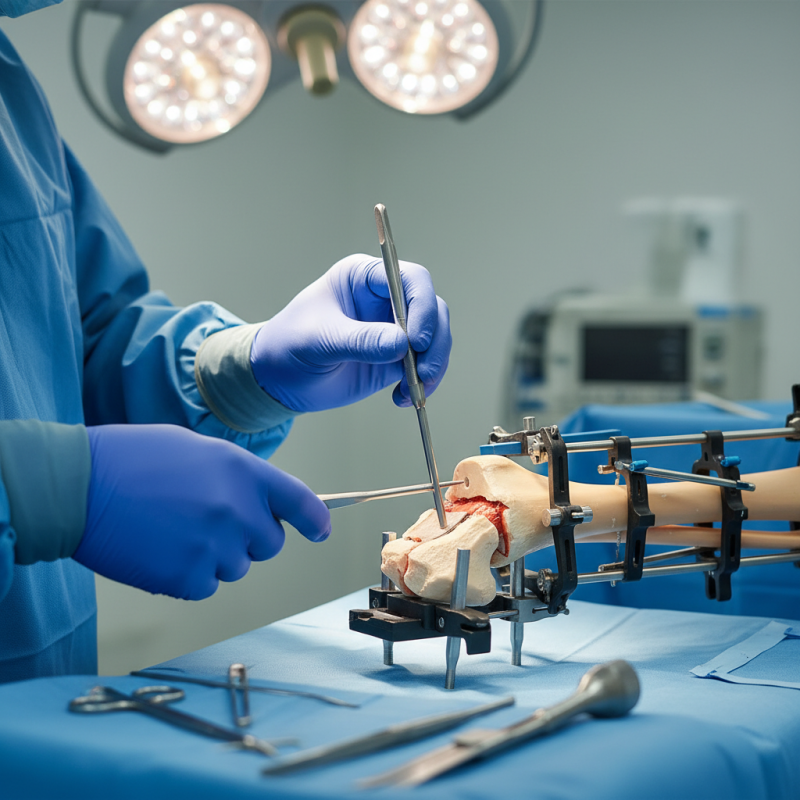
Understanding Intramedullary Nailing for Fracture Fixation
Intramedullary nailing is a popular technique for fracture fixation, particularly for long bone fractures. This method involves inserting a metal rod into the central canal of the bone. The rod stabilizes the fracture and promotes healing. It can reduce recovery time and improve patients' outcomes. However, the technique requires great precision and skill from the surgeon.
Understanding the anatomy is crucial. Each bone has unique structures that must be navigated during the procedure. Complications can arise, such as infections or malalignment. These risks emphasize the need for thorough preoperative planning. Surgeons must also consider patient factors, like bone quality and overall health, before proceeding.
Post-surgery, monitoring is essential. Patients may experience pain or limited mobility during recovery. Regular follow-ups help ensure that healing is progressing. If complications appear, further interventions may be necessary. This reality reminds both patients and surgeons that healing is a journey, not just a destination.
Fracture Fixation Outcomes Using Intramedullary Nailing
Indications for Using Intramedullary Nails in Fracture Treatment
Intramedullary nails are widely used in fracture treatment. They are particularly beneficial for certain types of fractures. For example, they are ideal for diaphyseal fractures of long bones, such as the femur or tibia. These nails provide stability while allowing for early mobilization. They also minimize soft tissue damage.
Intramedullary nails can be used in specific cases. Indications include comminuted fractures, unstable fractures, or fractures in patients with compromised bone quality. However, it’s crucial to assess each case carefully. Not all fractures will benefit from this method. Some fractures may require different approaches. Always consult with an orthopedic specialist.
Tips for using intramedullary nails include proper sizing of the nail. Ensure that the nail fits the medullary canal adequately. Also, consider the patient's activity level. Early mobilization is key, but too much activity too soon can hinder healing. Monitoring signs of infection is essential. Be aware of the potential complications. Always evaluate the fracture healing progress through regular imaging.
How to Use Nail Intramedullari for Fracture Fixation?
| Indication | Description | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Femoral Shaft Fractures | Fractures of the mid-shaft of the femur can be stabilized with intramedullary nails. | Minimal soft tissue damage, less intramedullary invasion, and promotes fracture union. | Proper surgical technique is crucial to avoid complications like non-union or malunion. |
| Tibia Fractures | Intramedullary nailing is commonly used for both closed and some open tibia fractures. | Effective stabilization, easy to insert, and provides axial stability. | Careful monitoring for potential infection and compartment syndrome post-operation. |
| Humerus Fractures | Intramedullary nails are effective for proximal and mid-shaft humeral fractures. | Allows early mobilization and is less invasive than plate fixation. | Requires a learning curve for proper technique and may have a risk of radial nerve injury. |
| Major Trauma Cases | Nailing is used in polytrauma patients to stabilize femur and tibia fractures. | Allows for rapid stabilization and enables earlier physical therapy. | Assessment of other injuries is critical before the procedure. |
Preparation and Planning for Intramedullary Nail Procedure
When preparing for an intramedullary nail procedure, thorough planning is crucial. Understanding the patient's overall health is the first step. Consider factors like age, bone quality, and other existing injuries. According to recent studies, about 90% of patients with femoral fractures benefit from intramedullary fixation techniques. However, the patient's unique anatomy should guide the surgeon’s approach.
Tips: Always evaluate imaging data closely. X-rays and CT scans reveal critical details. They provide insight into fracture alignment and comminution. Missing this can lead to improper nail placement, resulting in complications.
Patient consent and education are equally important. Communicate the procedure's risks and benefits clearly. Research shows that over 30% of patients experience anxiety before surgery. Addressing concerns can improve outcomes and build trust. It's also wise for the surgical team to rehearse the procedure. This practice ensures everyone is prepared for unexpected difficulties during surgery.
Tips: Create a checklist for instruments and implants. A ready set can minimize delays. Seamless teamwork enhances efficiency. Keep in mind that not every case goes as planned. Reflect on each procedure to learn and improve future techniques. Each surgery is a step toward mastering this complex skill.
Step-by-Step Technique for Inserting Intramedullary Nails
Inserting intramedullary nails is a common technique for fracture fixation. The procedure requires precision and careful planning. Start with appropriate imaging to assess the fracture. Mark the entry point on the bone carefully to obtain the best angle. These details matter significantly during the procedure.
After marking, use a drill to create a pilot hole. The size of the drill bit is crucial; it should match the nail diameter closely. Once the hole is ready, the nail must be inserted methodically. There should be no rush at this stage. Check the alignment throughout the insertion to avoid misplacement. Sometimes, unexpected resistance may occur. Adjust your technique accordingly and don’t hesitate to reassess your angle.
Once the nail is in place, secure it with locking screws. This step is critical for stability. Take your time to ensure everything is aligned well. Some surgeons may overlook this, but taking extra care here can prevent future complications. Be aware of potential issues like nail migration or malalignment. Reflecting on your approach can enhance your skills over time.
Post-Operative Care and Complications Management After Nailing
Post-operative care is critical after nail intramedullary fixation. Patients need to understand the importance of following instructions. Keeping the surgical site clean reduces infection risk. Dressing changes are vital. It’s easy to forget, but regularly monitoring the wound helps detect issues early.
Complications can arise. Delayed healing is one concern. Excessive swelling or pain might signal problems. Patients should be vigilant about any unusual symptoms. Physical therapy can help regain strength. However, pushing too hard too soon can lead to setbacks. Balance is key in rehabilitation.
Communication with healthcare providers is essential. If there are concerns, reach out. It’s important not to ignore changes in the body. Adapting to a recovery routine takes patience. Reflection on daily progress can boost morale. Understanding the journey aids in healing effectively.
